The Hydrology and Water Use research team members published an article in the Water journal entitled ‘Ice Regime of the Kozłowa Góra Reservoir (Southern Poland) as an Indicator of Changes of the Thermal Conditions of Ambient Air’.
Measurements and observations of ice phenomena in the Kozłowa Góra reservoir have been carried out since 1964. In 1964-2015, there was a decrease in the number of days with an ice cover (by 8.6 days per decade) and a decrease in the maximum and average thickness of lake ice (by 2.0 cm and 1.2 cm per decade, respectively). The small average depth and capacity of the reservoir are reflected in the rapid freezing rate of the reservoir, and the location results in a longer time of ice cover and greater thickness and later dates of ice melting, in relation to lakes located in northern Poland.
Solarski, M.; Rzętała, M. Ice Regime of the Kozłowa Góra Reservoir (Southern Poland) as an Indicator of Changes of the Thermal Conditions of Ambient Air. Water 2020, 12, 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092435
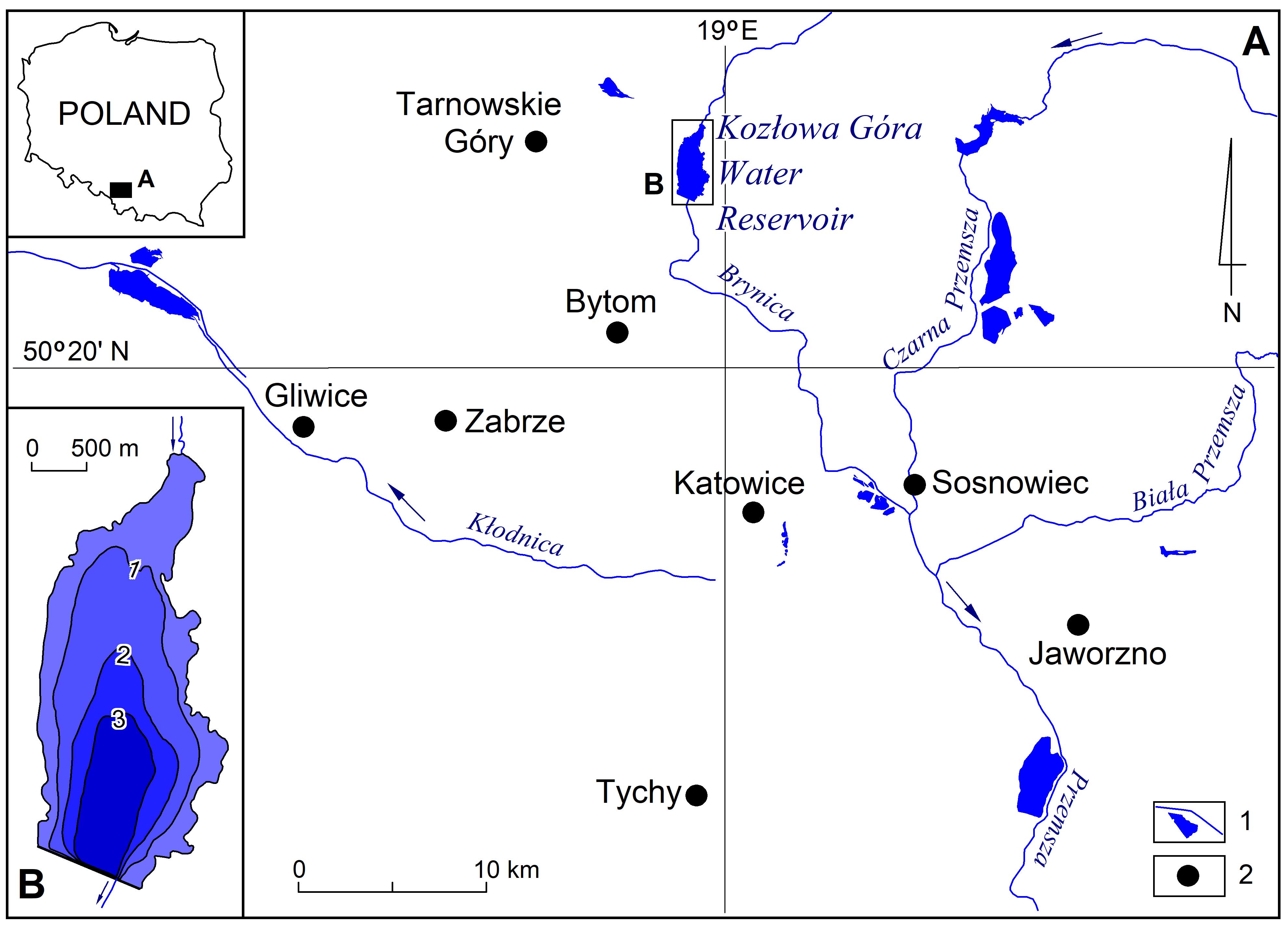
Fig.1
Location of the Kozłowa Góra reservoir (A) together with its bathymetric plan (B): 1—water courses and water reservoirs, 2—major cities.

Fig 2.
Changes in average air temperature in the winter half-year (XI–IV) in the hydrological years 1964–2015 at the Katowice weather station and values of the winter NAODJFM index (D—December, J—January, F—February, M—March): 1—NAODJFM index, 2—average air temperature, 3—average air temperature trend.
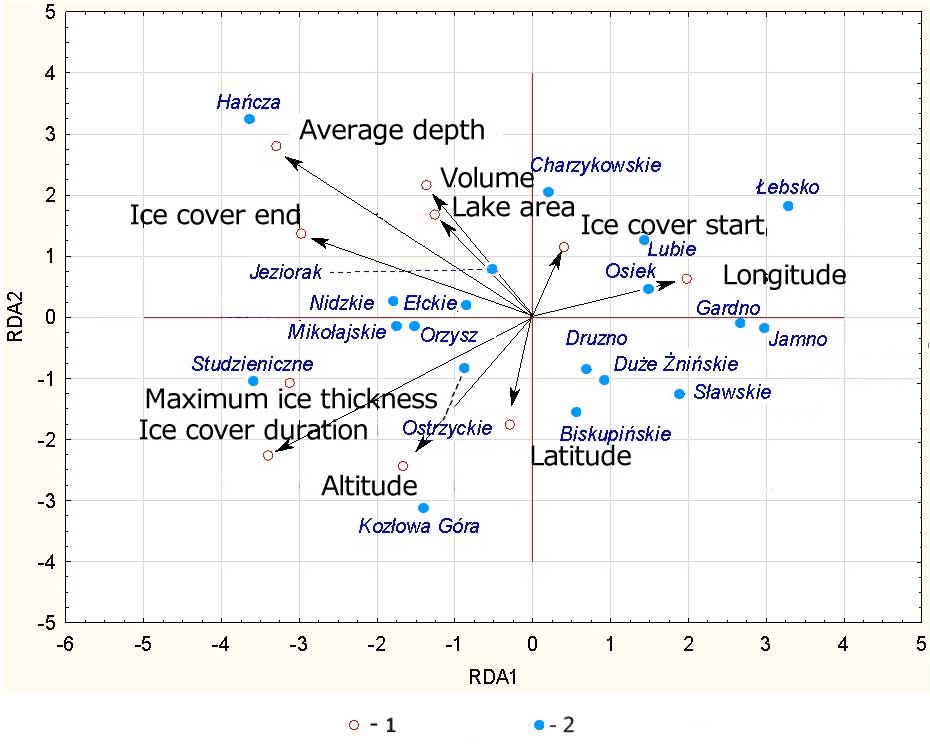
Fig. 5.
RDA biplots illustrating relations between environmental variables and selected parameters of lake ice phenology for the Kozłowa Góra reservoir and lakes in northeastern Poland and northwestern Poland: 1—correlated variables, 2—lakes examined.





